Vascular Health

Peripheral Vascular Disease
PAD (Peripheral Vascular Disease) is a condition of the arteries in your circulatory system. Plaque builds up in your arteries over time and may cause blockages. Since the blood flow is restricted by these blockages, your arms, legs, and other organs may not receive oxygenated blood. In many cases, your body may be able to re-route the blood around the blockage by creating new arteries called collateral arteries. If the blockage goes untreated, then you may form symptoms, which is your body’s way of telling you it needs help. There are many treatment options for PAD, but if you ignore your symptoms for too long, it can lead to non-healing wounds and/or limb loss.
Risk Factors:
Age >65, Diabetes, Obesity, Smoking, High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, History of PAD
Primary Symptoms:
Leg pain while walking, leg cramping, discoloration (foot may be blue), non-healing wounds, temperature change in legs or feet, hair loss on legs, leg numbness or weakness
Diagnosis:
Consult with a Vascular Provider, a peripheral ultrasound
Treatment Options:
Diet and Exercise, quit smoking, minimally invasive in-office procedure, open surgery in hospital
The SAC team specializes in the surgical treatment of PAD. This treatment can be performed in-office as a minimally invasive, surgical procedure.
Vein Disease
Vein disease is a medical condition of the veins known as Venous Insufficiency Disease or Venous Reflux Disease. Many people think that varicose veins are a sign of Venous Reflux Disease, but this is not always the case. Venous Reflux Disease is when the perforators in your vein grow weak and struggle to return de-oxygenated blood back to the heart. Sometimes the excess blood pools and causes discomfort, or in worse cases, venous ulcers. The pooled blood can also cause your veins to enlarge, known as varicose veins. The conflicting issue is that not all people with varicose veins have Venous Reflux Disease, and not all people with Venous Reflux Disease develop varicose veins. An estimated 40% of the US population has Venous Reflux Disease.
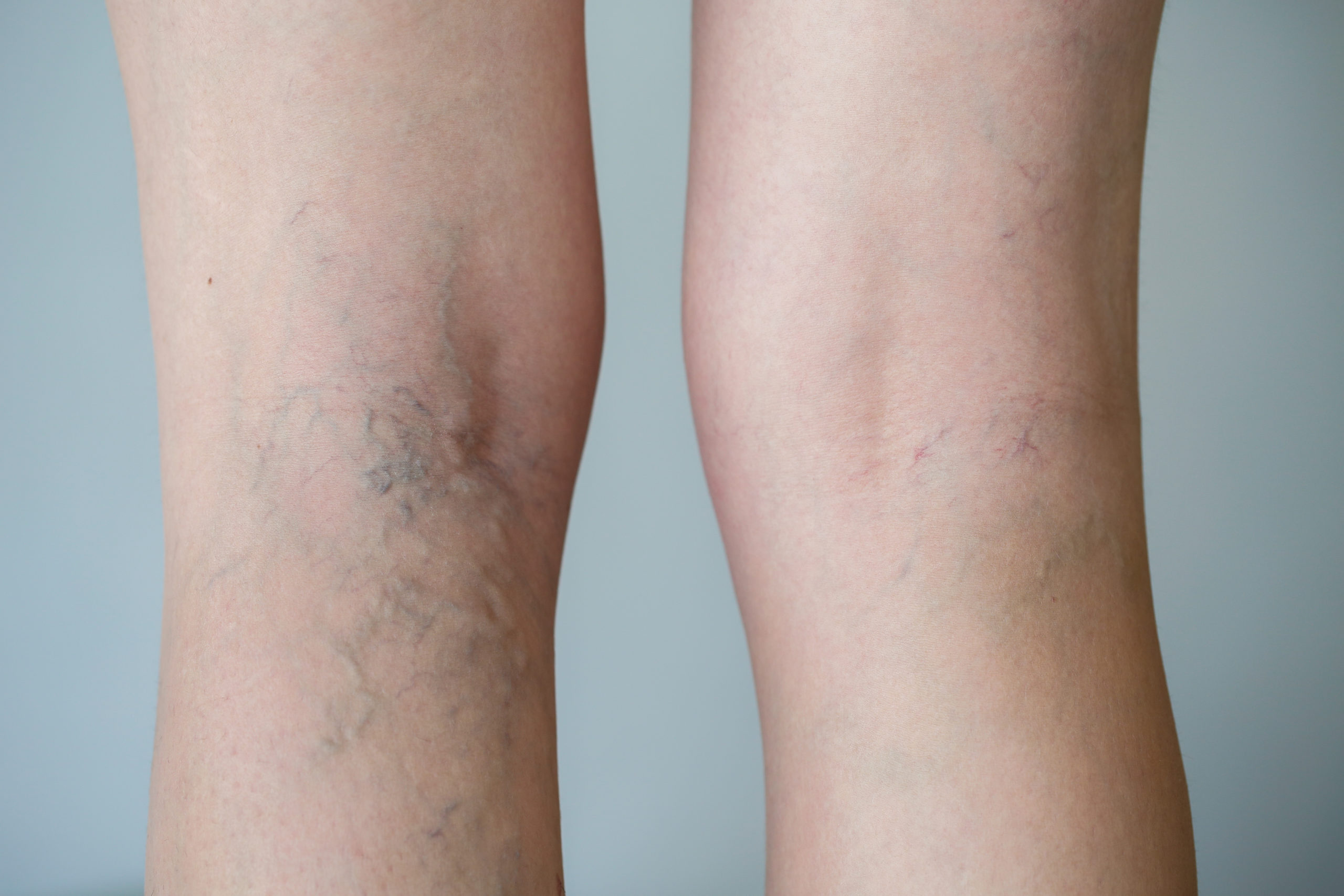
Risk Factors:
Pregnancy, genetics, age, sitting or standing for long periods of time (occupational hazard), height (tall people)
Primary Symptoms:
Swelling in the legs and/or feet, aching or tiredness in the legs, non-healing wounds, flaking or itching on the skin of the legs
Diagnosis:
Consult with Vascular Provider, venous reflux ultrasound, vein mapping
Treatments:
Compression stockings, exercise, elevate legs, avoid sitting or standing for too long, minimally invasive in-office procedures (laser or radio frequency ablation).
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep Vein Thrombosis
DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) is the medical term for a blood clot, usually located in the legs. DVT’s are common but should be treated immediately so they don’t dislodge and travel into the lungs, causing a more severe condition known as a Pulmonary Embolism (PE).
Risk Factors:
History of Blood clots, surgery, obesity, non-ambulatory people, pregnancy
Primary Symptoms:
Swelling, redness, pain, warm to the touch
Diagnosis:
DVT ultrasound
Treatment Options:
Compression stockings, medication, and more severe cases may require intervention but rarely surgery
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
AAA (Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm) is a condition where the aortic artery gets enlarged and, in worse cases, may rupture. It is located above your hips in your lower abdomen and supplies blood to the vital organs and legs.
Risk Factors:
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, hardening of the arteries
Primary Symptoms:
Very rare to have symptoms, but there may be pain in the lower abdomen or back. Nausea may also occur.
Diagnosis:
Consult with a Vascular Provider, AAA ultrasound
Treatment Options:
Minimally invasive endovascular procedure
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm

Carotid Artery Disease

Carotid Artery Disease
CAD (Carotid Artery Disease) is a vascular condition of the carotid arteries. These arteries run on either side of your neck and transport oxygen-rich blood from your heart to your brain. Similar to PAD, CAD occurs when one or both of your carotid arteries becomes blocked by an increased amount of plaque. Blocked carotid arteries can cause strokes if not monitored or treated properly.
Risk Factors:
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, hardening of the arteries
Primary Symptoms:
Very rare to have symptoms, but there may be symptoms of a stroke. Temporary loss of vision in one eye.
Diagnosis:
Consult with a Vascular Provider, Carotid ultrasound
Treatment Options:
Diet and exercise, surgery, or a carotid stent
Dialysis Access
Dialysis access is when a vascular surgeon surgically implants an access point into your vein or artery. There are several ways to create access to the blood for dialysis; a fistula, a graft, or a catheter.
Contact us today to learn more about a new, minimally invasive way to create a fistula in-office, without surgery.
Dialysis Access